Latest
Strengthening tourism ethnocentrism in emerging tourism destinations
The Tafter Journal editorial board has selected this article as one of the most interesting among the journals affiliated with DOAJ – The Directory of Open Access Journals.…
Italian culture: The need for emancipation from political dynamics
The recent incident involving the former Minister of Culture, Sangiuliano, risks slowing down public and private investments in the cultural and creative…
The global music landscape, the role of record companies, and ongoing innovations in the industry
This is a summary of the IFPI Global Music Report 2024 on the state of the global music industry. Like previous editions, it…
The diffuse museum: art, territorial identity, social practices and the narration of places. The MUDIAC Project.
The aim of this paper is to provide a contribution on cultural projects aiming at territorial identity and narration, tools capable of…
The eARTh project
In a world brimming with complexities and challenges, the power of art to educate, illuminate, and foster empathy remains a beacon of…
Mind the Gap
The cultural sector needs managers. There is no other reason why the cultural sector is not the great thing of this era. The entire sector has changed since…
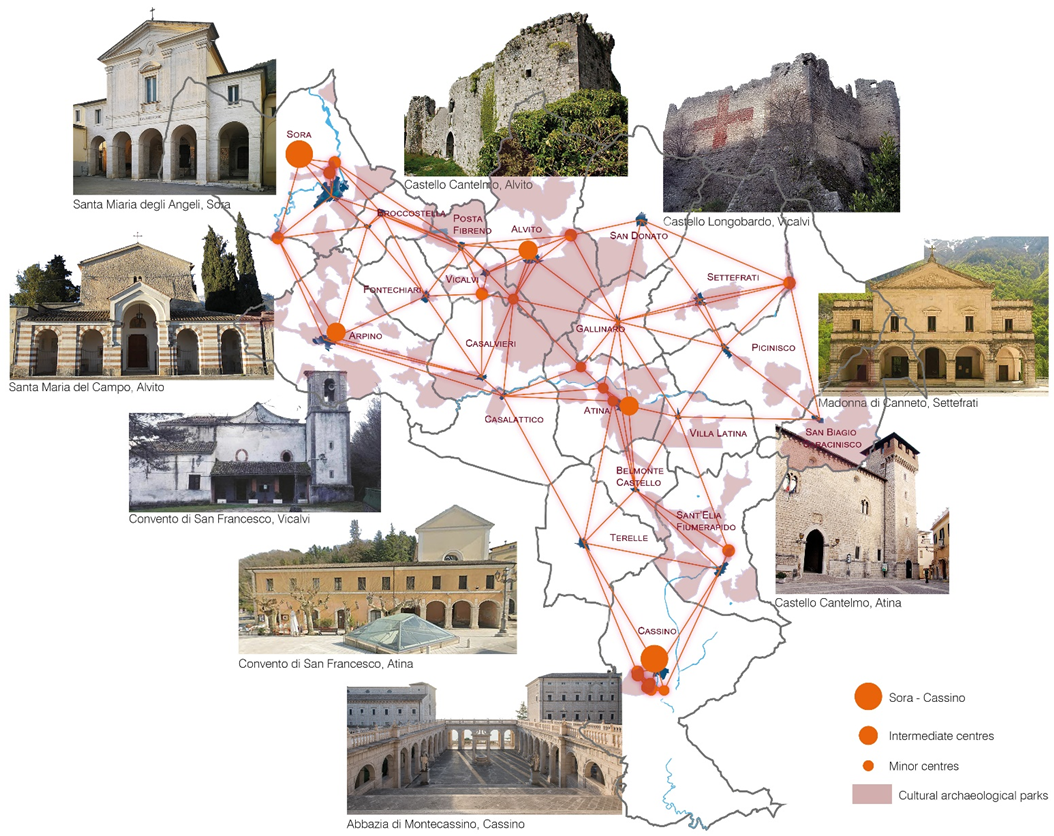
Knowledge and exploitation of local resources: the historical centers of the Comino Valley
This contribution is focused on an area located in the southern area of the Lazio region called “Valle di Comino” that has…
Commercial Districts and Corporate Planning: an international review
The literature review aims at representing the different applications of the concept of the Trade District by comparing similar experiences on an…
Large-scale urban regeneration threatening historic urban landscapes. The Liverpool Waters development and the loss of a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The city of Liverpool has undergone repeated processes of urban transformation and urban regeneration over the last half a century. The city…
Reinventing the wheel: why museums should learn more about their visitors
Have you ever wondered why everybody underlines the relevance of private information and privacy policies? One of the most astonishing answers could…